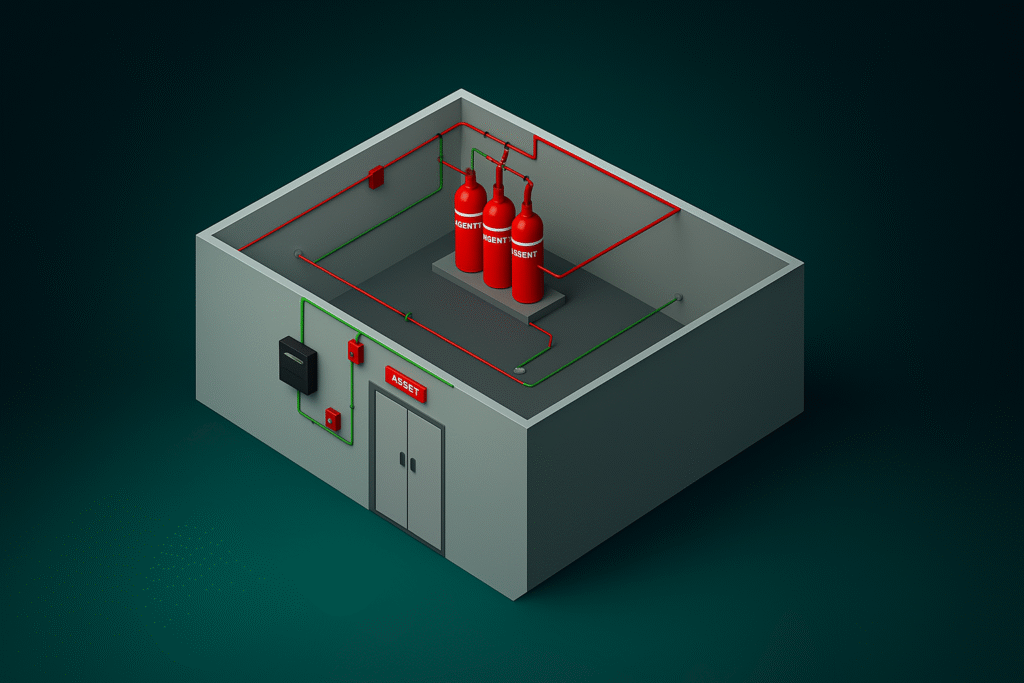
The Role of Biogas Plants in Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Biogas plants play an important role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions by turning organic waste into renewable energy, thus minimizing harmful gases released into the atmosphere. This blog explains in simple terms how biogas plants contribute to mitigating climate change, the mechanisms behind emission reductions, and their broader environmental impact. What is a Biogas Plant? A biogas plant is a facility that processes organic waste—such as food scraps, farm manure, and plant material—using natural bacteria in a sealed environment without oxygen. This fermentation process produces biogas, mainly composed of methane and carbon dioxide. The biogas can be used as clean energy for cooking, heating, or electricity generation. How Do Biogas Plants Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions? 1. Capturing Methane from Waste Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, far stronger than carbon dioxide in trapping heat in the atmosphere. When organic waste decomposes naturally in landfills or open areas, it releases methane into the air. A biogas plant captures this methane during the fermentation process, preventing it from escaping into the atmosphere. 2. Using Renewable Energy Instead of Fossil Fuels Biogas produced in the plant can replace fossil fuels like coal, oil, or natural gas. Burning fossil fuels releases carbon stored underground for millions of years, adding to atmospheric carbon dioxide. Biogas, however, comes from recently living organic matter, so the carbon dioxide it releases is part of the natural carbon cycle, making it more sustainable. 3. Reducing Waste and Pollution By turning waste into energy, biogas plants reduce the amount of organic waste sent to landfills or open dumping grounds, where uncontrolled decomposition releases greenhouse gases and pollutes soil and water. This helps lower overall environmental pollution. Additional Environmental Benefits of Biogas Plants The Broader Impact on Climate Change Studies estimate biogas could reduce global greenhouse gas emissions by up to